Learn about the MOA of abrocitinib.
CIBINQO is an oral, small molecule JAK inhibitor that works inside the cell1,2
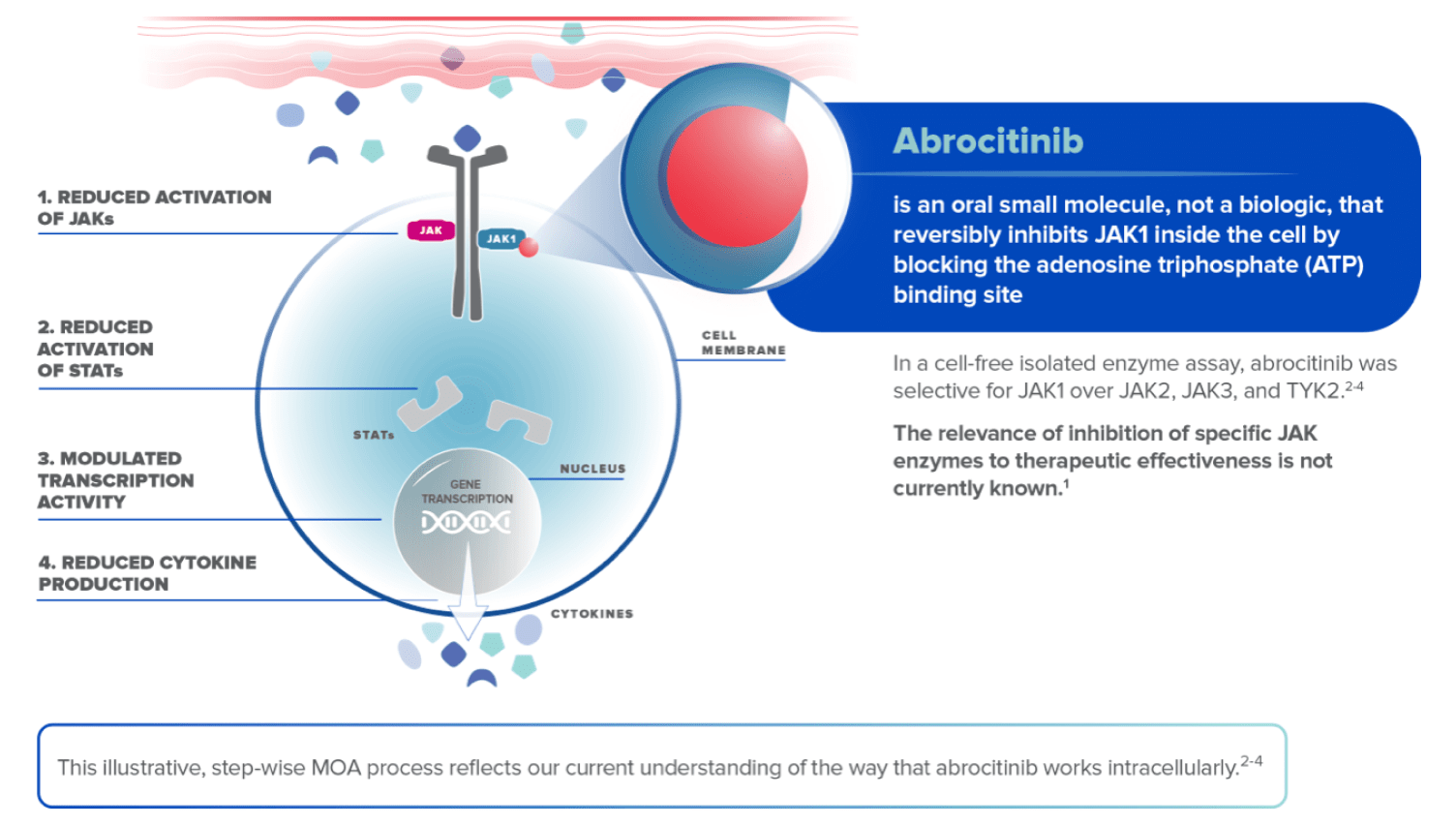
Please note that the molecules and cell structures are for illustrative purposes only.
JAK=Janus kinase; STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription; TYK2=tyrosine kinase 2.
Discover what could be contributing to the inflammation, itch, and skin barrier disruption experienced by your patients with AD.
Many cytokines contribute to dysregulated immune processes, signs and symptoms in atopic dermatitis5
Some key cytokines signal through the JAK/STAT pathway and are believed to drive inflammation, itch, and skin barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis6-8
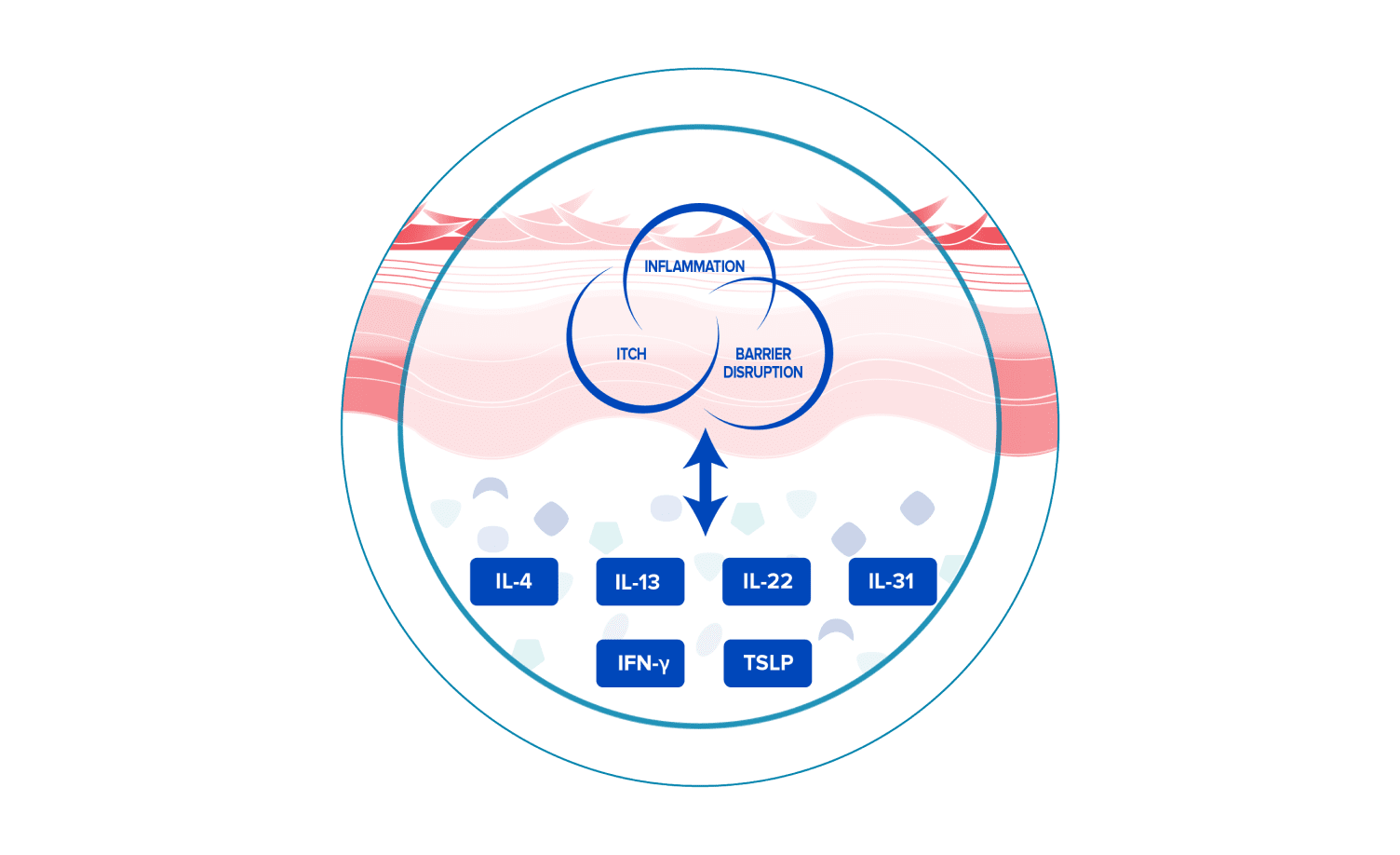
Cytokines signal through a variety of receptor families.9
Apart from those listed here, other cytokines are also involved in the pathogenesis of AD.5,6,10
A mechanistic look at the JAK/STAT pathway9,11,12
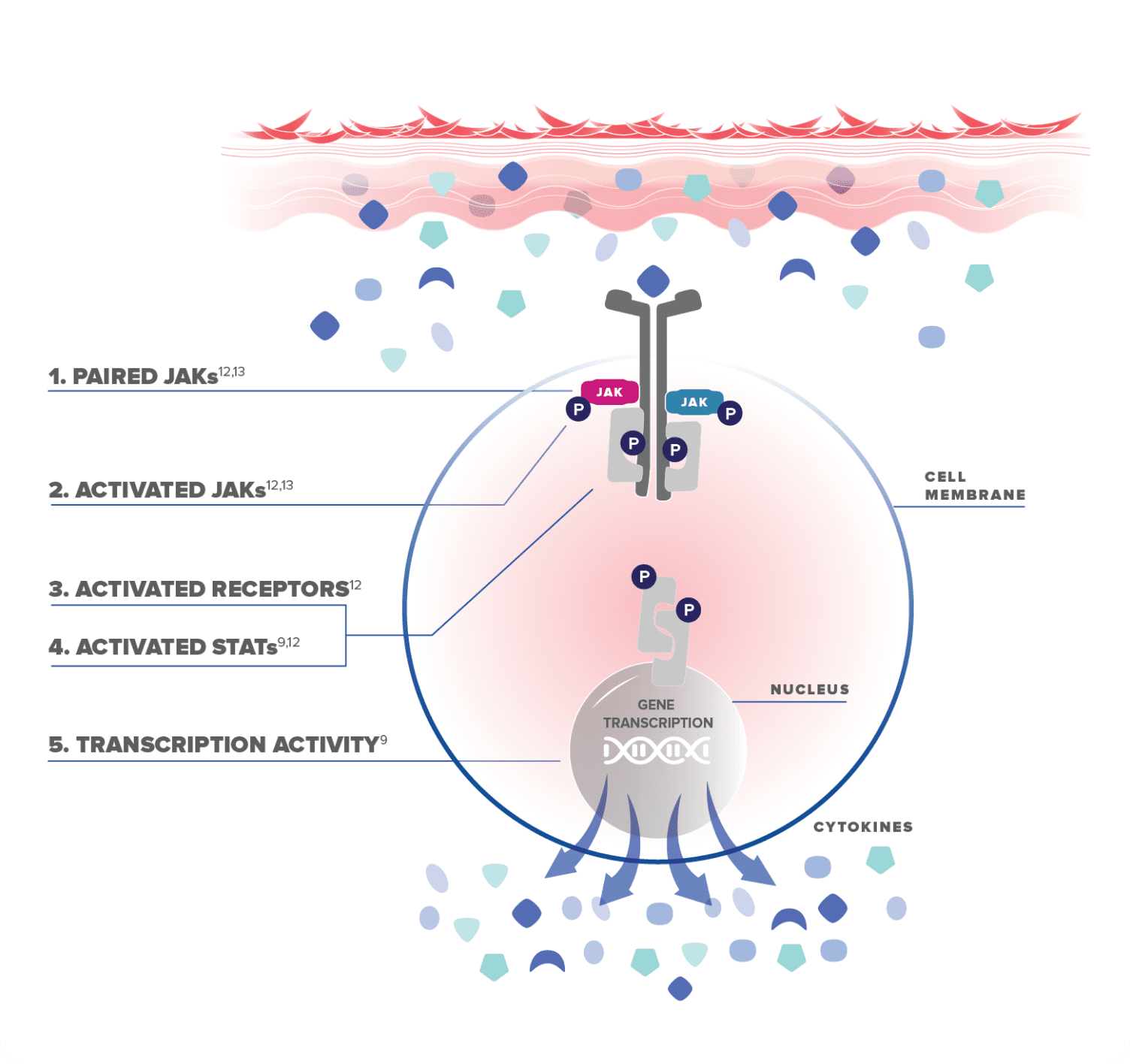
Please note that the molecules and cell structures are for illustrative purposes only.
AD=atopic dermatitis; JAK=Janus kinase; STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription; IL=interleukin; IFN=interferon;
TSLP=thymic stromal lymphopoietin; P=phosphate.
Learn about the MOA of abrocitinib.
CIBINQO is an oral, small molecule JAK inhibitor that works inside the cell1,2

Please note that the molecules and cell structures are for illustrative purposes only.
JAK=Janus kinase; STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription; TYK2=tyrosine kinase 2.
Discover what could be contributing to the inflammation, itch, and skin barrier disruption experienced by your patients with AD.
Many cytokines contribute to dysregulated immune processes, signs and symptoms in atopic dermatitis5
Some key cytokines signal through the JAK/STAT pathway and are believed to drive inflammation, itch, and skin barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis6-8

Cytokines signal through a variety of receptor families.9
Apart from those listed here, other cytokines are also involved in the pathogenesis of AD.5,6,10
A mechanistic look at the JAK/STAT pathway9,11,12

Please note that the molecules and cell structures are for illustrative purposes only.
AD=atopic dermatitis; JAK=Janus kinase; STAT=signal transducer and activator of transcription; IL=interleukin; IFN=interferon;
TSLP=thymic stromal lymphopoietin; P=phosphate.
References:
- Cibinqo (abrocitinib) latest approved Isareli prescribing information.
- Vazquez ML, Kaila N, Strohbach JW, et al. Identification of N-{cis-3-[Methyl(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino]cyclobutyl}propane-1-sulfonamide (PF-04965842): a selective JAK1 clinical candidate for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. J Med Chem. 2018;613:1130-1152.
- Gooderham MJ, Forman SB, Bissonnette R, et al. Efficacy and safety of oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor abrocitinib for patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(12):1371-1379.
- Gooderham MJ, Forman SB, Bissonnette R, et al. Supplementary appendix to: Efficacy and safety of oral Janus kinase 1 inhibitor abrocitinib for patients with atopic dermatitis: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(12):1371-1379.
- Langan SM, Irvine AD, Weidinger S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2020;396(10253):345-360.
- Howell MD, Kuo FI, Smith PA. Targeting the Janus kinase family in autoimmune skin diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2342.
- Paller AS, Kabashima K, Bieber T. Therapeutic pipeline for atopic dermatitis: end of the drought? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;140(3):633-643.
- Ishizaki M, Muromoto R, Akimoto T, et al. Tyk2 is a therapeutic target for psoriasis-like skin inflammation. Int Immunol. 2014;26(5):257-267.
- Clark JD, Flanagan ME, Telliez JB. Discovery and development of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for inflammatory diseases. J Med Chem. 2014;57(12):5023-5038.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, Kabashima K, Irvine AD. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4(1):1. doi:10.1038/s41572-018-0001-z
- Hammarén HM, Virtanen AT, Raviola J, Silvennoinen O. The regulation of JAKs in cytokine signaling and its breakdown in disease. Cytokine. 2019;118:48-63.
- Damsky W, King BA. JAK inhibitors in dermatology: The promise of a new drug class. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(4):736-744.
- Bao L, Zhang H, Chan LS. The involvement of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in chronic inflammatory skin disease atopic dermatitis. JAK-STAT. 2013;2:e24137. doi:10.4161/jkst.24137

