CIBINQO offers the flexibility to change the dose if needed1-3
Dosing considerations

- Recommended dose is 200 mg orally, once daily.
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
- During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
- The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered. The maximum daily dose is 200 mg.
- Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.

- Cibinqo can be used with or without medicated topical therapies for atopic dermatitis.

- Take the medicine with or without food at approximately the same time each day.
- If patients experience nausea, it sometimes helps to take the medicine with food.

- Swallow CIBINQO tablets whole with water.
- Do not crush, split, or chew CIBINQO tablets.
Limitations of Use: CIBINQO is not recommended for use in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic immunomodulators, or with other immunosuppressants.
Pills not shown at actual size.
The peak plasma concentration of abrocitinib is reached within 1 hour. The elimination half-life of abrocitinib is about 5 hours. Steady-state plasma concentration of abrocitinib are achieved within 48 hours after once-daily administration.
Dose adjustments for patients with renal or hepatic impairment1
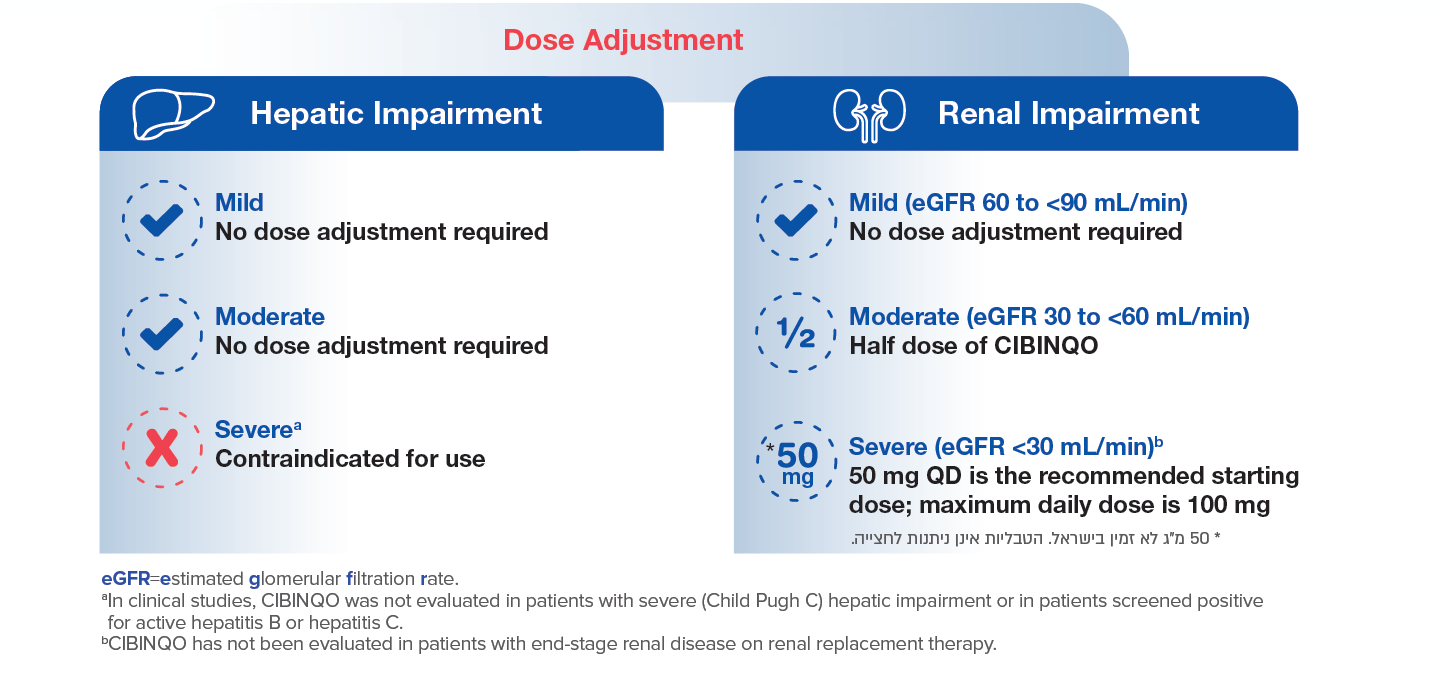
Renal impairment: No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild renal impairment, i.e. estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 60 to < 90 mL/min. Abrocitinib has not been studied in patients with eGFR < 40 mL/min. The recommended dose is based on extrapolation. In patients with moderate (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min) renal impairment, the recommended dose of abrocitinib should be reduced by half to 100 mg or 50 mg once daily. In patients with severe (eGFR < 30 mL/min) renal impairment, 50 mg once daily is the recommended starting dose. The maximum daily dose is 100 mg. Abrocitinib has not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on renal replacement therapy.
Dose adjustments for drug-drug interactions1,4
Not an exhaustive list of drug-drug interactions; the label must be reviewed in order to understand other potential drug-drug interactions with CIBINQO.
*50 mg tablets are not available in Israel. Tablets should not be split or crushed.
PPI - In patients receiving acid reducing agents (e.g. antacids, proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists), 200 mg once daily dose of abrocitinib should be considered.
GFR was estimated by the MDRD formula.
CYP=cytochrome P450; eGFR=estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESRD=end-stage renal disease;
P-gp=P-glycoprotein; MDRD=Modification of Diet in Renal Disease.
References:
- Cibinqo (abrocitinib) latest approved Isareli prescribing information.
- Goriacko P, Veltri KT. Adverse drug effects involving the gastrointestinal system (pharmacist perspective). Geriatric Gastroenterology. Springer, Cham. 2021. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-30192-7_10
- Leslie T. Nausea and vomiting. Patient Assessment in Clinical Pharmacy. Springer, Cham. 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-11775-7_6
- Levine GN, Bates RE, Bittl JA, et al. 2016 ACC/AHA Guideline Focused Update on duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(10):1082-1115. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.03.513

