JADE COMPARE was a phase 3 pivotal trial that evaluated the efficacy and safety of CIBINQO in combination with TCS vs placebo in patients with moderate to severe AD.1,2
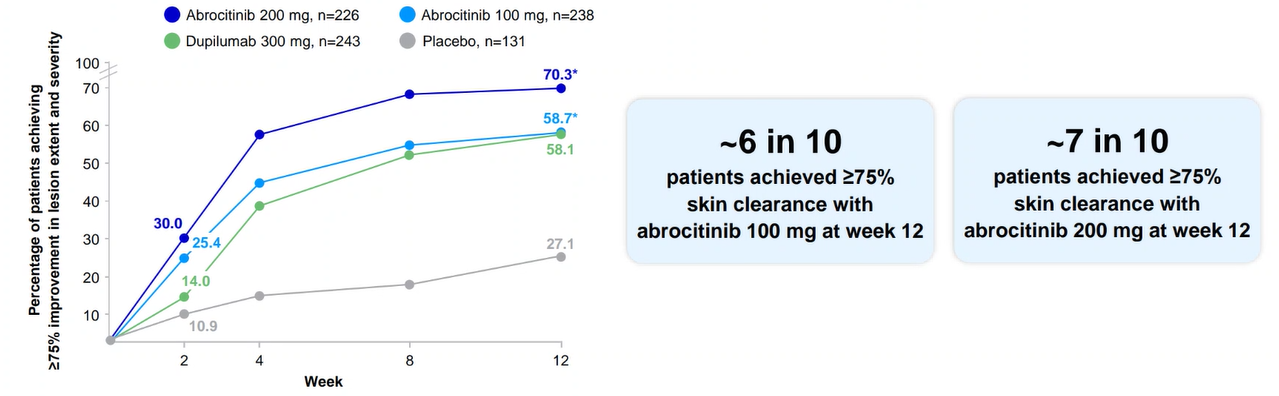
Powerful skin clearance results vs placebo at week 121,2

JADE COMPARE: EASI-75 for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo (co-primary endpoint)
Results are not to be interpreted as evidence of superiority, noninferiority, or similarity between CIBINQO and dupilumab. Dupilumab was included as an active control.
The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
A EASI-75 at week 16 (key secondary endpoint): 58% with CIBINQO 100 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 70% with CIBINQO 200 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 29% with placebo; and 63% with dupilumab.
Consider CIBINQO for refractory, moderate-to-severe AD when response to other systemics is inadequate or these therapies are inadvisable.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. All missing responses were defined as non-responders. AD=atopic dermatitis; EASI-75=≥75% improvement in lesion extent and severity from baseline on the Eczema Area and Severity Index; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
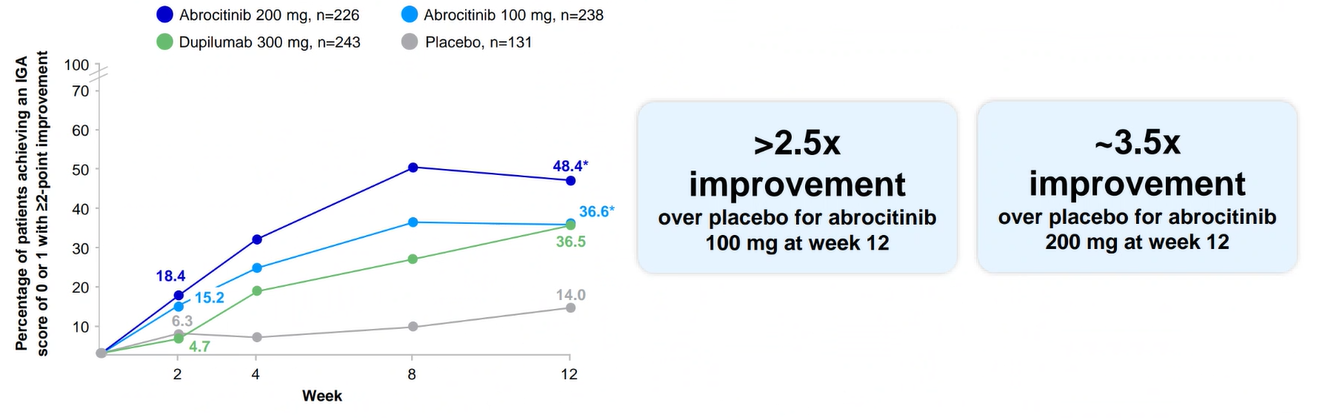
Clear or almost clear skin at week 121,2

JADE COMPARE: IGA response (0/1) for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo (co-primary endpoint)
Results are not to be interpreted as evidence of superiority, noninferiority, or similarity between CIBINQO and dupilumab. Dupilumab was included as an active control.
The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
A IGA 0/1 at week 16 (key secondary endpoint): 34.8% with CIBINQO 100 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 47.5% with CIBINQO 200 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 12.9% with placebo; and 37% with dupilumab.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. All missing responses were defined as non-responders.
A responder was defined as achieving IGA 0 or 1 and at least a 2-point improvement from baseline.
AD=atopic dermatitis; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
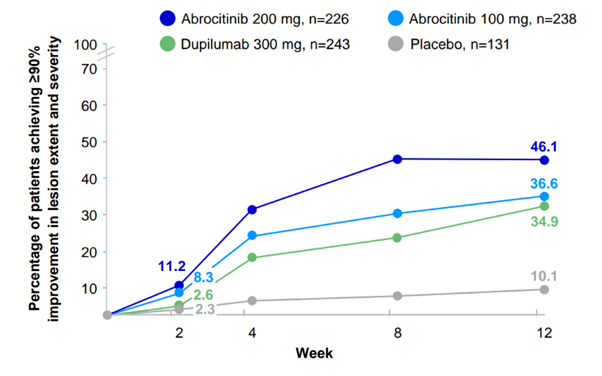
EASI-90 skin clearance results1,2

JADE COMPARE: EASI-90 for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo (secondary endpoint)
EASI-90 was a pre-specified secondary endpoint not controlled for multiplicity; thus, results cannot be interpreted as evidence of superiority, noninferiority or similarity between all treatment arms.
The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
A EASI-90 at week 16: 38% with CIBINQO 100 mg; 49% with CIBINQO 200 mg; 11% with placebo; and 39% with dupilumab.
Patients who completed the study but may have had missing data were excluded from those time points in the NRI analysis.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication.
AD=atopic dermatitis; EASI-90=≥90% improvement in lesion extent and severity from baseline on the Eczema Area and Severity Index; NRI=non-responder imputation; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
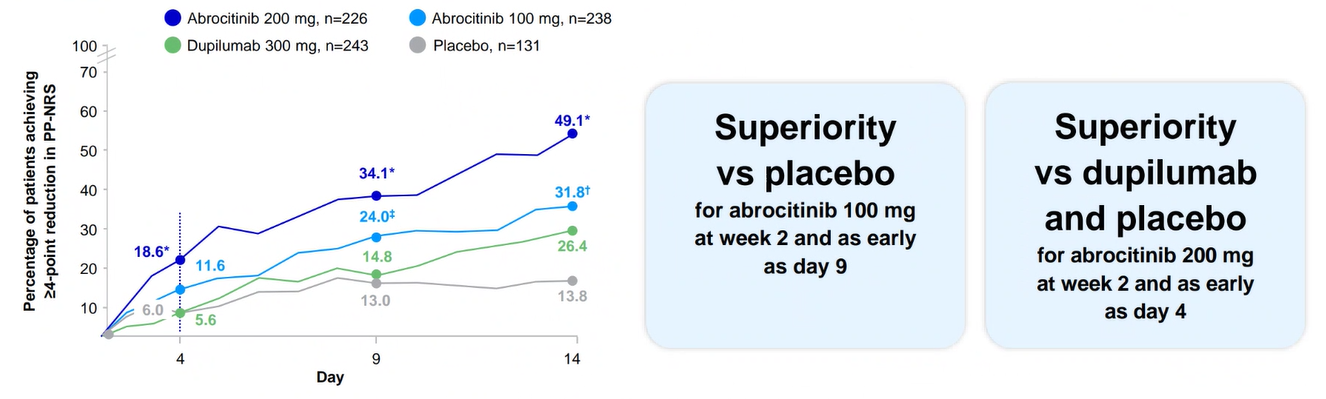
Itch reduction at week 21,2

JADE COMPARE: PP-NRS4 for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo and dupilumab (key secondary endpoint)
The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
- At week 2, similar proportions of subjects achieved itch relief for CIBINQO 100 mg and dupilumab
- At week 2, higher proportions of subjects achieved itch relief with 200 mg compared to dupilumab
* Based on a weekly average analysis, superiority was not met for CIBINQO 100 mg vs placebo or dupilumab at week 2.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. All missing responses were defined as non-responders.
Consider CIBINQO for refractory, moderate-to-severe AD when response to other systemics is inadequate or these therapies are inadvisable.
AD=atopic dermatitis; PP-NRS4=≥4-point reduction from baseline on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
Powerful skin clearance results vs placebo at week 121,2

JADE COMPARE: EASI-75 for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo (co-primary endpoint)
Results are not to be interpreted as evidence of superiority, noninferiority, or similarity between CIBINQO and dupilumab. Dupilumab was included as an active control.

The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
A EASI-75 at week 16 (key secondary endpoint): 58% with CIBINQO 100 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 70% with CIBINQO 200 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 29% with placebo; and 63% with dupilumab.
Consider CIBINQO for refractory, moderate-to-severe AD when response to other systemics is inadequate or these therapies are inadvisable.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. All missing responses were defined as non-responders. AD=atopic dermatitis; EASI-75=≥75% improvement in lesion extent and severity from baseline on the Eczema Area and Severity Index; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
Clear or almost clear skin at week 121,2

JADE COMPARE: IGA response (0/1) for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo (co-primary endpoint)
Results are not to be interpreted as evidence of superiority, noninferiority, or similarity between CIBINQO and dupilumab. Dupilumab was included as an active control.

The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
A IGA 0/1 at week 16 (key secondary endpoint): 34.8% with CIBINQO 100 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 47.5% with CIBINQO 200 mg (P<0.0001 vs placebo); 12.9% with placebo; and 37% with dupilumab.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. All missing responses were defined as non-responders.
A responder was defined as achieving IGA 0 or 1 and at least a 2-point improvement from baseline.
AD=atopic dermatitis; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
EASI-90 skin clearance results1,2

JADE COMPARE: EASI-90 for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo (secondary endpoint)
EASI-90 was a pre-specified secondary endpoint not controlled for multiplicity; thus, results cannot be interpreted as evidence of superiority, noninferiority or similarity between all treatment arms.

The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
A EASI-90 at week 16: 38% with CIBINQO 100 mg; 49% with CIBINQO 200 mg; 11% with placebo; and 39% with dupilumab.
Patients who completed the study but may have had missing data were excluded from those time points in the NRI analysis.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication.
AD=atopic dermatitis; EASI-90=≥90% improvement in lesion extent and severity from baseline on the Eczema Area and Severity Index; NRI=non-responder imputation; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
Itch reduction at week 21,2

JADE COMPARE: PP-NRS4 for CIBINQO 100 mg or 200 mg vs placebo and dupilumab (key secondary endpoint)

The recommended starting dose is CIBINQO 200 mg once daily
- A starting dose of 100 mg once daily is recommended for patients ≥ 65 years of age and in patients at high risk for DVT/PE.
For other patients who may benefit from a starting dose of 100 mg, see sections 4.4 and 4.8 in the LPD. - During treatment, the dose may be decreased or increased based on tolerability and efficacy.
The lowest effective dose for maintenance should be considered.
The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. - Discontinuation of treatment should be considered in patients who show no evidence of therapeutic benefit after 24 weeks.
- At week 2, similar proportions of subjects achieved itch relief for CIBINQO 100 mg and dupilumab
- At week 2, higher proportions of subjects achieved itch relief with 200 mg compared to dupilumab
* Based on a weekly average analysis, superiority was not met for CIBINQO 100 mg vs placebo or dupilumab at week 2.
Full Analysis Set (FAS) was defined as all randomized subjects who received at least one dose of study medication. All missing responses were defined as non-responders.
Consider CIBINQO for refractory, moderate-to-severe AD when response to other systemics is inadequate or these therapies are inadvisable.
AD=atopic dermatitis; PP-NRS4=≥4-point reduction from baseline on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
Study design1,2,4,5
JADE COMPARE was a phase 3 pivotal trial that evaluated the efficacy and safety of CIBINQO in combination with TCS vs placebo in patients with moderate to severe AD.
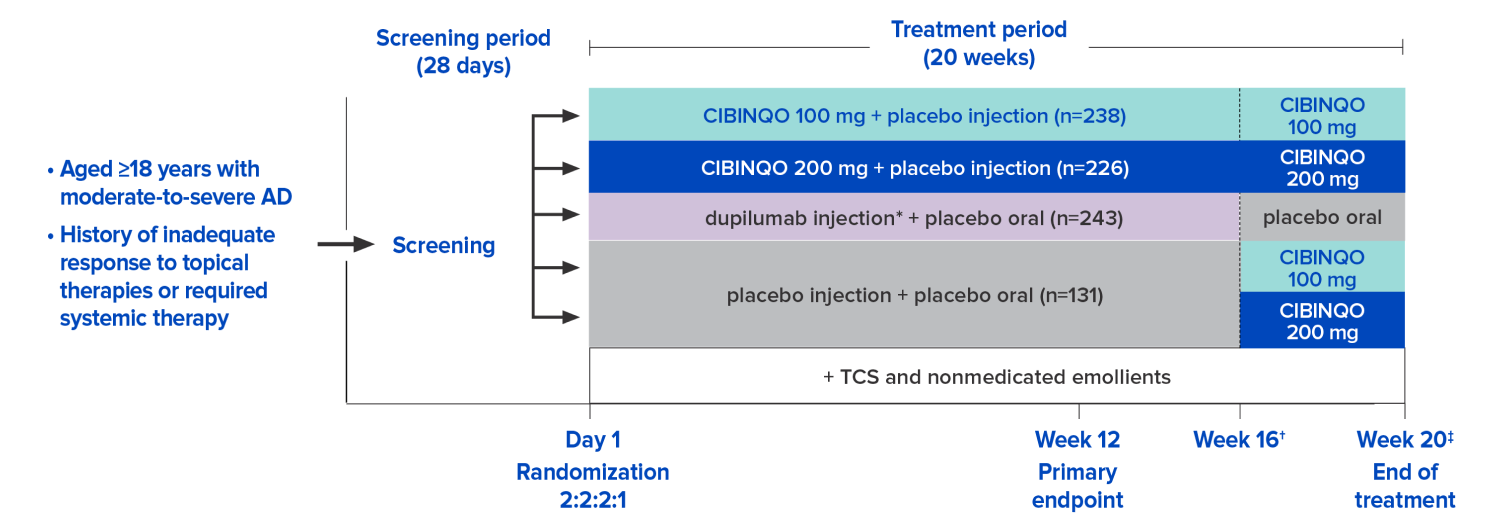
- Co-primary endpoints:
- EASI-75 response at week 12 vs placebo
- IGA 0/1 response with ≥2-point improvement at week 12 vs placebo
- Key secondary endpoints:
- PP-NRS4 response at week 2 vs dupilumab and vs placebo
- EASI-75 response at week 16 vs placebo
- IGA 0/1 response with ≥2-point improvement at week 16 vs placebo
* Dupilumab was an active control except for the one head-to-head endpoint of PP-NRS4 at week 2.
Subjects used nonmedicated emollient twice a day and medicated topical therapy, such as corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or PDE4 inhibitors, per protocol guidance, to treat active lesions during the study. The majority used corticosteroids with selective use of TCI and PDE4 inhibitors.
In JADE clinical trial program, EASI and IGA excluded scalp, palms, and soles from the assessment/scoring.
† Dupilumab or its matching placebo was administered for 16 weeks, with the final injection planned for week 14 to facilitate the washout of dupilumab prior to eligible subjects entering the long-term extension study.5
‡ At week 20, eligible subjects entered the long-term extension study (JADE EXTEND); ineligible subjects entered the 4-week off-treatment follow-up period.
AD=atopic dermatitis; EASI-75=≥75% improvement in lesion extent and severity from baseline on the Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; PDE4=phosphodiesterase-4; PP-NRS4=≥4-point reduction from baseline on the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale; TCI=topical calcineurin inhibitors; TCS=topical corticosteroids.
JADE COMPARE baseline characteristics2,4
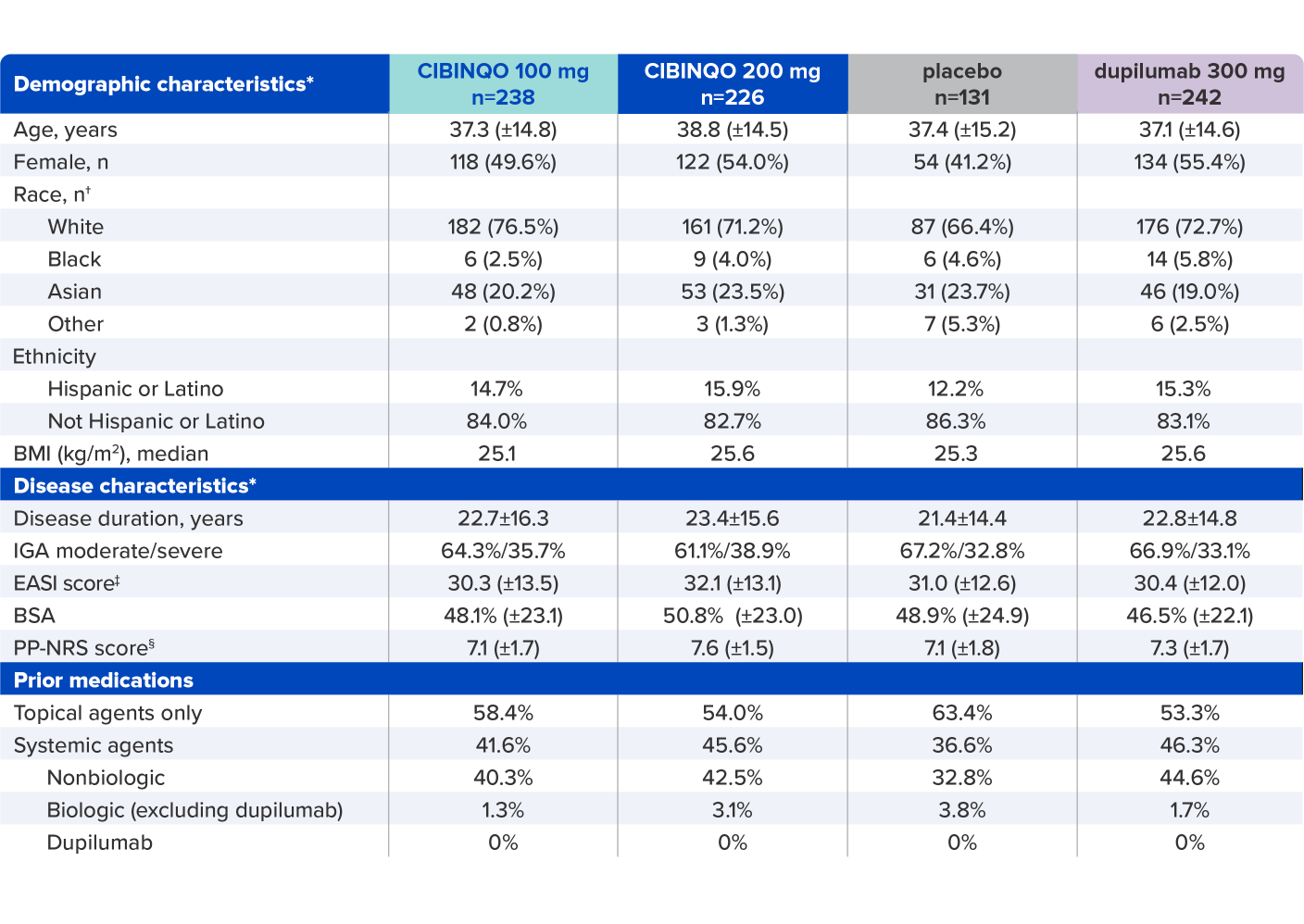
* Plus–minus values are means ± SD. Percentages may not total 100 because of rounding.
† Race was reported by the patients.
‡ Scores on EASI range from 0 to 72, with higher scores indicating more severe disease.
§
Scores on PP-NRS represent maximum itch severity in the previous 24 hours and range from 0 to 10, with higher scores representing more severe itch.
BMI=body mass index; BSA=body surface area; EASI=Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; PP-NRS=Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale; SD=standard deviation.
JADE COMPARE baseline characteristics2,4

* Plus–minus values are means ± SD. Percentages may not total 100 because of rounding.
† Race was reported by the patients.
‡ Scores on EASI range from 0 to 72, with higher scores indicating more severe disease.
§
Scores on PP-NRS represent maximum itch severity in the previous 24 hours and range from 0 to 10, with higher scores representing more severe itch.
BMI=body mass index; BSA=body surface area; EASI=Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; PP-NRS=Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale; SD=standard deviation.
JADE COMPARE inclusion/exclusion criteria2-3
- Inclusion criteria
- ≥18 years of age
- Clinically diagnosed with chronic AD for ≥1 year, confirmed by the Hanifin and Rajka criteria of AD at the screening and baseline visits*
- Have a documented history of inadequate response to previous topical therapy, or were subjects for whom topical treatments were medically inadvisable, or require systemic therapies to control their disease
- Moderate-to-severe AD defined as BSA ≥10%, IGA ≥3, EASI ≥16, and PP-NRS ≥4 at the baseline visit
- Exclusion criteria
- Active forms of other inflammatory skin diseases
- Prior treatment with any JAK inhibitors
- Prior treatment with dupilumab and/or a history of hypersensitivity, intolerance, AE, or allergic reaction associated with prior exposure to the excipients of dupilumab
- Vaccination with, or exposure to, a live or attenuated vaccine within 6 weeks prior to the first dose
- Participation in other clinical studies involving investigational drug(s) within 8 weeks prior to study entry
- Uncontrolled, clinically significant laboratory abnormality that could affect study interpretation
- Any major psychiatric condition
- Unwillingness to discontinue current AD medications prior to the study
- Requiring treatment with prohibited medications during the study
- Medical history of thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy or platelet dysfunction, or Q wave interval abnormalities
- Presence or history of certain infections, cancers, lymphoproliferative disorders, and other medical conditions at the discretion of the investigator
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Women of childbearing potential who are unwilling to use contraception
* Criteria include ≥3 of the basic features of pruritus; typical morphology and distribution, including flexural lichenification or linearity in adults and facial and extensor involvement in infants and children; chronic or chronically relapsing dermatitis; and personal or family history of atopy (asthma, allergic rhinitis, AD); along with ≥3 of 23 minor features specified in the criteria.
AD=atopic dermatitis; AE=adverse event; BSA=body surface area; EASI=Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; JAK=Janus kinase; PP-NRS=Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale.
JADE COMPARE inclusion/exclusion criteria2-3
- Inclusion criteria
- ≥18 years of age
- Clinically diagnosed with chronic AD for ≥1 year, confirmed by the Hanifin and Rajka criteria of AD at the screening and baseline visits*
- Have a documented history of inadequate response to previous topical therapy, or were subjects for whom topical treatments were medically inadvisable, or require systemic therapies to control their disease
- Moderate-to-severe AD defined as BSA ≥10%, IGA ≥3, EASI ≥16, and PP-NRS ≥4 at the baseline visit
- Exclusion criteria
- Active forms of other inflammatory skin diseases
- Prior treatment with any JAK inhibitors
- Prior treatment with dupilumab and/or a history of hypersensitivity, intolerance, AE, or allergic reaction associated with prior exposure to the excipients of dupilumab
- Vaccination with, or exposure to, a live or attenuated vaccine within 6 weeks prior to the first dose
- Participation in other clinical studies involving investigational drug(s) within 8 weeks prior to study entry
- Uncontrolled, clinically significant laboratory abnormality that could affect study interpretation
- Any major psychiatric condition
- Unwillingness to discontinue current AD medications prior to the study
- Requiring treatment with prohibited medications during the study
- Medical history of thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy or platelet dysfunction, or Q wave interval abnormalities
- Presence or history of certain infections, cancers, lymphoproliferative disorders, and other medical conditions at the discretion of the investigator
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Women of childbearing potential who are unwilling to use contraception
* Criteria include ≥3 of the basic features of pruritus; typical morphology and distribution, including flexural lichenification or linearity in adults and facial and extensor involvement in infants and children; chronic or chronically relapsing dermatitis; and personal or family history of atopy (asthma, allergic rhinitis, AD); along with ≥3 of 23 minor features specified in the criteria.
AD=atopic dermatitis; AE=adverse event; BSA=body surface area; EASI=Eczema Area and Severity Index; IGA=Investigator’s Global Assessment; JAK=Janus kinase; PP-NRS=Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale.
References:
- Cibinqo (abrocitinib) latest approved Isareli prescribing information.
- Data on file. Pfizer Inc; New York, NY.
- Howell MD, Kuo FI, Smith PA. Targeting the Janus kinase family in autoimmune skin diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2342.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al; for the JADE COMPARE Investigators. Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:1101-1112.
- Bieber T, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI, et al; for the JADE COMPARE Investigators. Supplement to: Abrocitinib versus placebo or dupilumab for atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(12):1101-1112.

